Reversing Gingivitis Naturally: Evidence-Based Home Remedies That Work
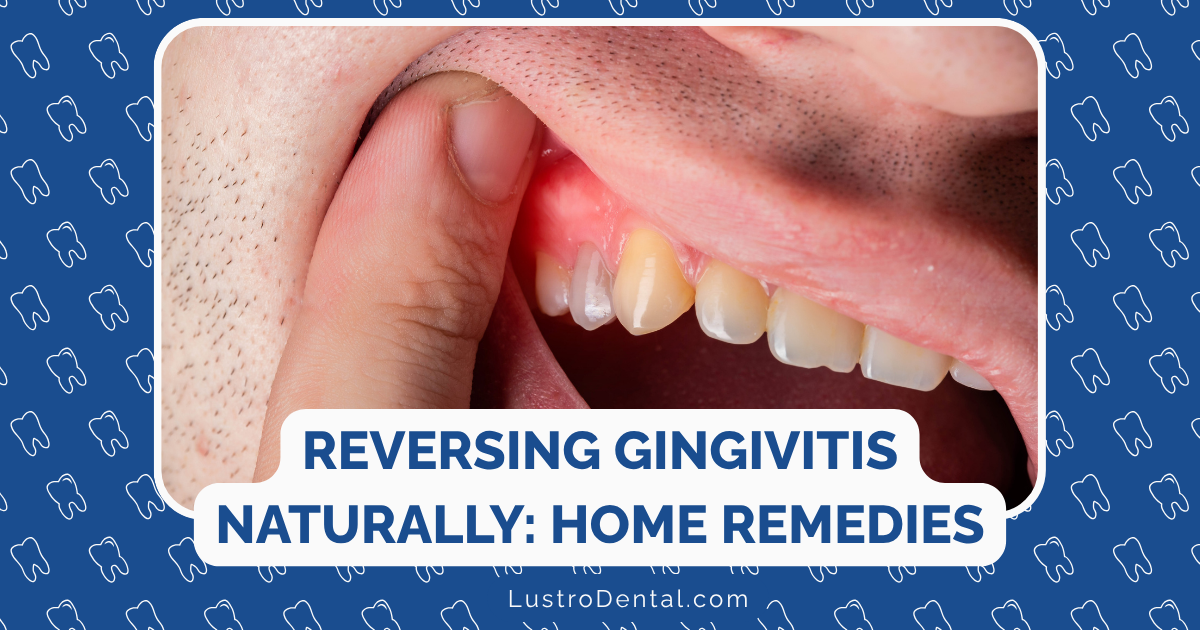
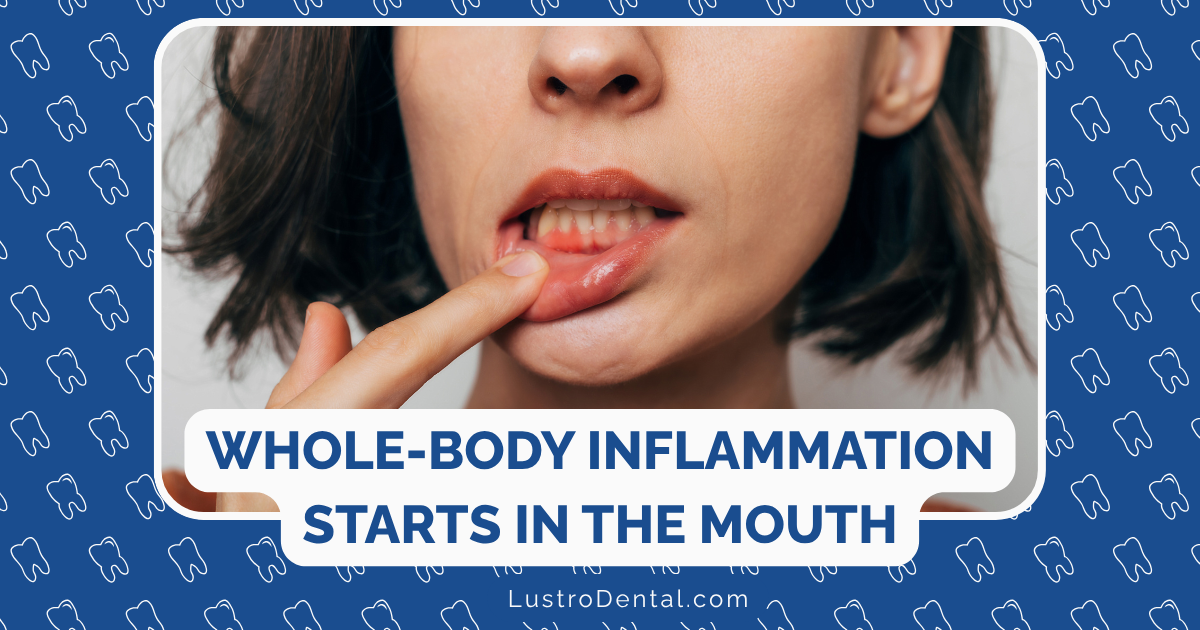
When patients notice their gums bleeding during brushing or flossing, they often ask me about natural ways to address gingivitis before it progresses to more serious periodontal disease. While professional dental care remains essential, there are indeed evidence-based natural approaches that can help reverse early-stage gingivitis and support gum health.
Gingivitis—characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums—affects nearly half of American adults. The good news is that this early stage of gum disease is completely reversible with proper care. In this article, I’ll focus on natural remedies that have scientific research backing their effectiveness, separating proven solutions from popular myths.
Understanding Gingivitis: The Foundation for Natural Treatment
Before diving into remedies, it’s important to understand what we’re treating. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums caused primarily by bacterial plaque buildup along the gumline. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, which involves irreversible bone loss around the teeth.
The key to reversing gingivitis naturally is to:
- Reduce bacterial plaque
- Decrease inflammation
- Support the body’s natural healing processes
With these goals in mind, let’s examine the most effective evidence-based natural approaches.
Evidence-Based Natural Remedies for Gingivitis
1. Salt Water Rinse: Simple Yet Effective
The Evidence: A 2017 study found that salt water rinses can be as effective as chlorhexidine (a prescription antimicrobial mouthwash) in reducing dental plaque. Salt water creates an alkaline environment that inhibits bacterial growth and promotes healing.
How to Use: Dissolve half a teaspoon of sea salt in 8 ounces of warm water. Swish for 30 seconds, then spit. Repeat 2-3 times daily, especially after meals.
Why It Works: According to research published in PubMed Central, salt water rinses alter the biology of harmful bacteria while promoting oral wound healing. They also help reduce inflammation, ease pain, and remove food particles.
2. Aloe Vera: Nature’s Soothing Anti-inflammatory
The Evidence: A 2023 study found that aloe vera was as effective as chlorhexidine in reducing plaque and gingivitis. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing gingival inflammation.
How to Use: You can use pure aloe vera gel directly on the gums or as a mouthwash. For a mouthwash, mix 2 tablespoons of aloe vera gel with water, swish for 30 seconds, and spit. Use twice daily.
Why It Works: According to a systematic review in PMC, aloe vera contains compounds with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immune-modulating properties. A clinical trial with 45 subjects showed significant decreases in gingival index and sulcus bleeding index after three months of aloe vera mouthwash use.
3. Tea Tree Oil: Powerful Antimicrobial Properties
The Evidence: A 2020 study indicated that tea tree oil mouthwash shows promise for treating gingivitis. Research has found that it can reduce plaque and improve gum health due to its antimicrobial properties.
How to Use: Add 2-3 drops of tea tree oil to a cup of warm water and use as a mouthwash. Alternatively, add a drop to your toothpaste before brushing. Important: Never use undiluted tea tree oil directly on gums, as it can cause irritation.
Why It Works: Tea tree oil (Melaleuca alternifolia) contains compounds with significant antimicrobial activity. A study found that tea tree oil mouthwash led to a mean plaque index decrease to 5.5%, demonstrating its effectiveness against oral bacteria associated with gingivitis.
4. Turmeric Gel: Anti-inflammatory Powerhouse
The Evidence: Multiple clinical trials have shown that turmeric-based gels and mouthwashes can significantly reduce gingival inflammation and plaque. A 2021 study found turmeric exhibited similar anti-plaque and anti-inflammatory properties as chlorhexidine.
How to Use: Make a paste by mixing 1/4 teaspoon of turmeric powder with a few drops of water or coconut oil. Apply to the gums and leave for 5-10 minutes before rinsing. Alternatively, use commercially available turmeric gels designed for oral use.
Why It Works: According to research in PMC, turmeric contains curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Clinical trials show that turmeric-based herbal dentifrice resulted in a 70-95% reduction in plaque, dental calculus, and gingivitis after 15 days of treatment.
5. Green Tea: Antioxidant-Rich Gum Protector
The Evidence: Studies published in the Journal of International Oral Health indicate that green tea can help reduce swelling and bleeding from gingivitis. Research shows that the catechins in green tea have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
How to Use: Drink 2-3 cups of unsweetened green tea daily. For direct application, brew strong green tea, allow it to cool, and use as a mouthwash.
Why It Works: Green tea is rich in catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been shown to inhibit the growth of periodontal pathogens. A 2012 study found that green tea catechins inhibit the growth of many harmful, gingivitis-causing bacteria.
6. Oil Pulling: Ancient Practice with Modern Evidence
The Evidence: While not as strongly supported as some other remedies, recent research does show benefits. A 2016 study found that oil pulling with sesame oil resulted in a 20% reduction in bacterial count and a 50% reduction in gingival and plaque index.
How to Use: Place 1 tablespoon of coconut or sesame oil in your mouth and swish for 15-20 minutes, then spit into the trash (not down the drain as it can clog pipes). Rinse thoroughly with warm water afterward. Best done in the morning on an empty stomach.
Why It Works: According to a meta-analysis in PMC, oil pulling can significantly reduce salivary bacterial colony counts. The mechanism is thought to involve the oil’s ability to “pull” bacteria from the mouth as well as the antimicrobial properties of the oils themselves, particularly coconut oil which contains lauric acid.
7. Hydrogen Peroxide Diluted Rinse: Oxygen-Releasing Antibacterial
The Evidence: A 2011 study indicated that subgingival irrigation with 3% hydrogen peroxide plays a role in inflammation control and reduction of gingival bleeding.
How to Use: Mix equal parts 3% hydrogen peroxide and water. Swish for 30 seconds and spit. Use no more than 2-3 times per week, as frequent use can irritate gums.
Why It Works: Hydrogen peroxide releases oxygen upon contact with tissues, creating an environment hostile to anaerobic bacteria (the type commonly associated with gum disease). It also helps remove debris from between teeth and along the gumline.
8. Dietary Supplements with Research-Backed Benefits
Several supplements have shown promise in clinical studies for improving gum health:
Vitamin C
The Evidence: A 2021 review indicated that vitamin C supplements reduced gum bleeding in individuals with gingivitis and diabetes.
How to Use: Aim for 500-1000 mg daily, preferably from food sources like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries. Supplements can be used if dietary intake is insufficient.
Why It Works: According to research in PMC, vitamin C is crucial for collagen synthesis, which helps maintain the integrity of gum tissue. Deficiency is strongly associated with severe gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
The Evidence: Studies show that CoQ10 supplementation can significantly reduce gum inflammation. A recent clinical trial demonstrated improvements in gingival index and bleeding on probing with CoQ10 supplementation.
How to Use: Typical dosages range from 100-200 mg daily, taken with food to enhance absorption.
Why It Works: CoQ10 is an antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress in the gums. Research has found that people with periodontal disease often have CoQ10 deficiency in their gum tissue.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The Evidence: A 2020 review showed significant improvements in periodontal disease measures among those taking omega-3 supplements.
How to Use: Aim for 1-2 grams daily of combined EPA and DHA from fish oil supplements, or consume fatty fish like salmon 2-3 times per week.
Why It Works: According to multiple studies, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. A clinical trial found that omega-3 supplementation led to a significant reduction in gingival inflammation, outperforming CoQ10 in direct comparisons.
Vitamin D
The Evidence: A 2020 review found that individuals with periodontal disease had lower blood levels of vitamin D compared to those without. Supplementation studies show improvements in periodontal parameters.
How to Use: Typical recommendations range from 1000-4000 IU daily, depending on current blood levels and sun exposure.
Why It Works: According to research in PMC, vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune function and bone metabolism. Studies have found that higher doses of vitamin D supplementation (25,000 IU/week) over six months showed greater reductions in clinical parameters of periodontal disease compared to controls.
9. Mediterranean Diet: A Comprehensive Approach
The Evidence: A randomized controlled trial showed that adherence to a Mediterranean diet for six weeks reduced gingival index and bleeding on probing scores.
How to Use: Focus on consuming:
- Abundant fruits and vegetables
- Olive oil as the primary fat source
- Fatty fish 2-3 times weekly
- Nuts and seeds
- Whole grains
- Limited red meat and processed foods
Why It Works: According to research in MDPI, the Mediterranean diet is rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, antioxidants, and nutrients that support gum health. The combination of omega-3 fatty acids, polyphenols, vitamins, and minerals creates a synergistic effect that reduces gingival inflammation.
Implementing an Evidence-Based Natural Approach
For the best results in reversing gingivitis naturally, I recommend a comprehensive approach that combines several of these evidence-based remedies:
Daily Routine for Reversing Gingivitis Naturally
Morning:
- Oil pulling with coconut oil (optional, 15-20 minutes)
- Brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush and natural toothpaste
- Salt water rinse
- Take supplements (vitamin C, CoQ10, omega-3, vitamin D as needed)
- Drink green tea with breakfast
After Meals:
- Rinse with salt water or diluted hydrogen peroxide (the latter only 2-3 times per week)
Evening:
- Brush with soft-bristled toothbrush
- Apply turmeric gel or aloe vera to gums
- Use tea tree oil mouthwash
- Take any remaining supplements
Weekly:
- Review your diet and ensure adequate intake of anti-inflammatory foods
- Check your gums for improvement in redness, swelling, and bleeding
What About Popular Remedies That Lack Evidence?
While researching natural remedies for gingivitis, you may encounter some popular suggestions that lack scientific support:
- Activated charcoal: Despite its popularity, there’s insufficient evidence supporting its effectiveness for gum health, and some research suggests it may be too abrasive for regular use.
- Apple cider vinegar: While often promoted for oral health, the high acidity can actually damage tooth enamel if used regularly.
- Essential oils (other than tea tree oil): Most haven’t been adequately studied for gingivitis treatment, though some like clove oil may have temporary pain-relieving properties.
- Baking soda pastes: While baking soda has some antibacterial properties, evidence specifically for gingivitis is limited, and improper use can be abrasive to gums.
When to See a Dentist
While these natural remedies can be effective for mild to moderate gingivitis, they should complement—not replace—professional dental care. See a dentist if:
- Your gums bleed regularly during brushing or flossing
- Your gums are very red, swollen, or painful
- You have persistent bad breath
- Natural remedies don’t improve symptoms within 2 weeks
- You notice gum recession or loose teeth
- It’s been more than 6 months since your last dental cleaning
The Bottom Line: Evidence-Based Natural Approaches Work
The research is clear: certain natural remedies can effectively help reverse gingivitis when used consistently and correctly. The strongest evidence supports:
- Salt water rinses
- Aloe vera applications
- Turmeric gel
- Tea tree oil mouthwash (properly diluted)
- Green tea consumption
- Targeted supplementation (vitamin C, vitamin D, omega-3s, CoQ10)
- Mediterranean diet
By combining these approaches with proper brushing and flossing, most cases of early gingivitis can be successfully reversed. Remember that consistency is key—natural remedies typically work more gradually than pharmaceutical options, so patience and persistence are essential.
Have you tried any of these evidence-based natural remedies for gingivitis? What was your experience? Share in the comments below!